Understanding adjectives that describe evil is crucial for effective communication, allowing us to convey the severity and nature of wickedness with precision. This article delves into the grammar of these adjectives, exploring their various forms, uses, and nuances.
Whether you’re a student, writer, or language enthusiast, this guide will enhance your vocabulary and improve your ability to express complex ideas related to morality and wrongdoing. Master the art of describing evil with accuracy and impact.
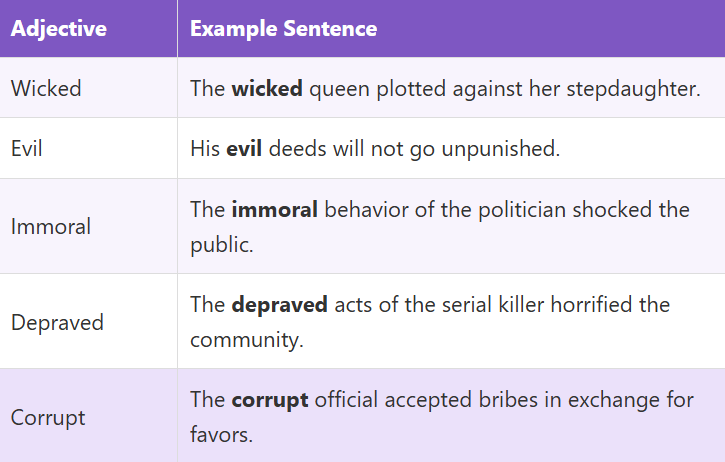
Table of Contents
- Definition of Adjectives for Evil
- Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
- Types and Categories of Adjectives for Evil
- Examples of Adjectives for Evil
- Usage Rules for Adjectives
- Common Mistakes with Adjectives
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Definition of Adjectives for Evil
Adjectives for evil are words that describe something or someone as being morally wrong, wicked, or harmful. They add detail and specificity to our understanding of negative actions, characters, or situations.
These adjectives can range from mild descriptions of naughtiness to severe indictments of profound wickedness, depending on the context and the intended impact.
In grammar, adjectives function as modifiers, providing additional information about nouns or pronouns. Adjectives for evil modify nouns or pronouns that represent evil entities, actions, or characteristics. For instance, in the phrase “a wicked plot,” the adjective “wicked” modifies the noun “plot,” indicating the evil nature of the plan. Similarly, in “a heinous crime,” the adjective “heinous” describes the severity and moral reprehensibility of the crime.
The context in which these adjectives are used significantly affects their interpretation. An adjective like “nasty,” while generally negative, might describe a minor unpleasantness in one context but could indicate a more serious form of evil in another.
Therefore, understanding the nuances and connotations of different adjectives is crucial for precise and effective communication. Exploring the different types and categories will give a deeper understanding of how to use them correctly.
Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
Adjectives, including those describing evil, typically precede the noun they modify. For example, “the sinister shadow” places the adjective “sinister” before the noun “shadow.” This is the most common structure in English.
However, adjectives can also appear after linking verbs like “is,” “are,” “was,” “were,” “seems,” “appears,” and “becomes.” In this case, they function as predicate adjectives. For example, “The plan was evil.” Here, “evil” follows the linking verb “was” and describes the subject “plan.”
Adjectives can also be modified by adverbs to intensify or qualify their meaning. For example, “extremely wicked” uses the adverb “extremely” to strengthen the adjective “wicked.” Similarly, “somewhat malevolent” uses “somewhat” to soften the adjective “malevolent.” Understanding how adverbs interact with adjectives allows for even greater precision in describing the degree of evil being conveyed.
Types and Categories of Adjectives for Evil
Adjectives for evil can be categorized based on the specific type of evil they describe. These categories help to differentiate the various nuances and degrees of wickedness.
Moral Depravity
These adjectives describe a state of extreme moral corruption or wickedness. They often imply a lack of ethical principles or a disregard for what is considered right and good.
Adjectives in this category include:
- Wicked
- Evil
- Immoral
- Depraved
- Corrupt
- Base
- Vile
- Nefarious
Destructive Force
This category includes adjectives that describe the capacity to cause significant harm or destruction. They emphasize the devastating impact of evil actions or entities.
Examples include:
- Devastating
- Ruinous
- Calamitous
- Catastrophic
- Deadly
- Lethal
- Destructive
- Baneful
Malevolent Intent
These adjectives focus on the intention to cause harm or suffering. They highlight the deliberate and malicious nature of evil actions or characters.
Adjectives in this category are:
- Malicious
- Sinister
- Baleful
- Diabolical
- Machiavellian
- Venomous
- Noxious
- Fiendish
Supernatural Evil
This category describes evil that is associated with supernatural forces or entities. These adjectives often evoke a sense of otherworldly dread or terror.
Examples are:
- Demonic
- Infernal
- Satanic
- Unholy
- Otherworldly
- Ghastly
- Nether
- Hellish
Corrupting Influence
These adjectives describe the power to degrade or undermine moral principles. They emphasize the insidious nature of evil that can spread and infect others.
Adjectives in this category include:
- Insidious
- Contaminating
- Pernicious
- Degenerate
- Seditious
- Subversive
- Rotten
- Tainted
Examples of Adjectives for Evil
The following tables provide examples of adjectives for evil used in sentences, categorized by the types discussed above. These examples illustrate how each adjective functions in context and conveys a specific nuance of evil.
Moral Depravity Examples
This table provides examples of adjectives describing moral depravity used in sentences. These examples demonstrate how each adjective functions in context to convey a sense of extreme moral corruption.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Wicked | The wicked queen plotted against her stepdaughter. |
| Evil | His evil deeds will not go unpunished. |
| Immoral | The immoral behavior of the politician shocked the public. |
| Depraved | The depraved acts of the serial killer horrified the community. |
| Corrupt | The corrupt official accepted bribes in exchange for favors. |
| Base | His base instincts drove him to betray his friends. |
| Vile | The vile rumors spread like wildfire through the town. |
| Nefarious | The nefarious scheme was designed to bankrupt the company. |
| Atrocious | The dictator committed atrocious crimes against humanity. |
| Heinous | The heinous murder case remained unsolved for years. |
| Reprobate | The reprobate gambler lost all his family’s savings. |
| Unconscionable | It was unconscionable to abandon the refugees in need. |
| Iniquitous | The iniquitous laws oppressed the minority population. |
| Perverse | His perverse sense of humor often offended people. |
| Shameless | The shameless politician lied without remorse. |
| Licentious | The licentious court was known for its scandalous affairs. |
| Debauched | His debauched lifestyle led to his downfall. |
| Dissolute | The dissolute prince squandered the kingdom’s wealth. |
| Flagrant | The flagrant disregard for the rules resulted in severe penalties. |
| Egregious | The egregious error cost the company millions. |
| Abhorrent | The abhorrent practices of the cult were exposed. |
| Despicable | His despicable actions made him an outcast. |
| Contemptible | The contemptible coward abandoned his post. |
| Ignominious | The team suffered an ignominious defeat. |
| Infamous | The pirate was an infamous figure in maritime history. |
Destructive Force Examples
This table provides examples of adjectives describing destructive force used in sentences. These examples demonstrate how each adjective emphasizes the devastating impact of evil actions or entities.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Devastating | The devastating earthquake left thousands homeless. |
| Ruinous | The ruinous war destroyed the country’s infrastructure. |
| Calamitous | The calamitous flood swept away entire villages. |
| Catastrophic | The catastrophic fire engulfed the entire building. |
| Deadly | The deadly virus spread rapidly across the globe. |
| Lethal | The lethal poison killed its victim instantly. |
| Destructive | The destructive storm caused widespread damage. |
| Baneful | The baneful influence of the dictator corrupted the nation. |
| Disastrous | The disastrous economic policies led to widespread poverty. |
| Detrimental | The detrimental effects of pollution are evident in the city. |
| Crippling | The crippling sanctions devastated the country’s economy. |
| Inimical | The inimical environment made survival difficult. |
| Noxious | The noxious fumes caused severe respiratory problems. |
| Pestilent | The pestilent disease ravaged the population. |
| Malignant | The malignant tumor threatened his life. |
| Traumatic | The traumatic experience left her scarred for years. |
| Wounding | His wounding words cut deep into her heart. |
| Corrosive | The corrosive acid ate through the metal. |
| Oppressive | The oppressive regime silenced all dissent. |
| Ruthless | The ruthless general showed no mercy to his enemies. |
| Ferocious | The ferocious storm raged for days. |
| Savage | The savage attack left the victim severely injured. |
| Brutal | The brutal dictator ruled with an iron fist. |
| Fierce | The fierce competition drove many companies out of business. |
Malevolent Intent Examples
This table provides examples of adjectives describing malevolent intent used in sentences. These examples demonstrate how each adjective focuses on the intention to cause harm or suffering.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Malicious | The malicious gossip was intended to ruin her reputation. |
| Sinister | A sinister figure lurked in the shadows. |
| Baleful | His baleful glare sent shivers down her spine. |
| Diabolical | The diabolical plan was designed to cause maximum chaos. |
| Machiavellian | The Machiavellian politician used any means necessary to gain power. |
| Venomous | Her venomous words dripped with hatred. |
| Noxious | The noxious rumors poisoned the atmosphere. |
| Fiendish | The fiendish laughter echoed through the castle. |
| Spiteful | Her spiteful remarks were meant to hurt him. |
| Vindictive | The vindictive tyrant sought revenge on his enemies. |
| Rancorous | The rancorous feud had lasted for generations. |
| Maleficent | The maleficent witch cast a dark spell. |
| Misanthropic | The misanthropic hermit shunned all human contact. |
| Perfidious | The perfidious ally betrayed his comrades. |
| Treacherous | The treacherous path led to a dangerous cliff. |
| Duplicitous | The duplicitous salesman deceived his customers. |
| Deceitful | His deceitful smile hid his true intentions. |
| Artful | The artful manipulator played everyone against each other. |
| Crafty | The crafty fox outsmarted the hounds. |
| Scheming | The scheming advisor plotted to overthrow the king. |
| Insidious | The insidious plan slowly undermined the company’s stability. |
| Calculating | The calculating villain always had a backup plan. |
| Cunning | The cunning spy gathered valuable intelligence. |
| Wily | The wily merchant drove a hard bargain. |
Supernatural Evil Examples
This table provides examples of adjectives describing supernatural evil used in sentences. These examples demonstrate how each adjective evokes a sense of otherworldly dread or terror.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Demonic | The demonic possession terrified the villagers. |
| Infernal | The infernal flames consumed the cursed forest. |
| Satanic | The Satanic rituals were performed in secret. |
| Unholy | The unholy relic radiated an aura of darkness. |
| Otherworldly | An otherworldly presence filled the ancient temple. |
| Ghastly | The ghastly apparition haunted the old house. |
| Nether | The nether regions were said to be the dwelling place of demons. |
| Hellish | The hellish landscape was filled with fire and brimstone. |
| Eldritch | An eldritch glow emanated from the forbidden artifact. |
| Occult | The occult practices were shrouded in mystery. |
| Preternatural | The preternatural abilities of the psychic were astounding. |
| Supernal | A supernal darkness descended upon the land. |
| Arcane | The arcane knowledge was guarded by a secret society. |
| Enchanted | The enchanted forest was filled with magical creatures. |
| Cursed | The cursed amulet brought misfortune to its owner. |
| Haunted | The haunted mansion was avoided by the locals. |
| Spectral | A spectral figure appeared in the moonlight. |
| Wraithful | The wraithful spirit sought revenge on its killer. |
| Phantasmal | A phantasmal glow surrounded the ancient ruins. |
| Grotesque | The grotesque gargoyle perched atop the cathedral. |
| Macabre | The macabre decorations were fitting for Halloween. |
| Monstrous | The monstrous creature emerged from the depths. |
| Abyssal | The abyssal darkness swallowed everything in its path. |
Corrupting Influence Examples
This table provides examples of adjectives describing corrupting influence used in sentences. These examples demonstrate how each adjective emphasizes the insidious nature of evil that can spread and infect others.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Insidious | The insidious propaganda slowly eroded public trust. |
| Contaminating | The contaminating influence of the gang spread through the school. |
| Pernicious | The pernicious effects of the drug addiction were devastating. |
| Degenerate | The degenerate practices of the cult were exposed. |
| Seditious | The seditious pamphlets incited the population to revolt. |
| Subversive | The subversive elements sought to undermine the government. |
| Rotten | The rotten core of the organization was finally revealed. |
| Tainted | The tainted evidence was thrown out of court. |
| Vitiating | The vitiating atmosphere of the office stifled creativity. |
| Corroding | The corroding effects of jealousy destroyed their friendship. |
| Undermining | The undermining tactics weakened the company’s position. |
| Deleterious | The deleterious impact of stress on health is well-documented. |
| Debasing | The debasing treatment of prisoners was condemned by human rights groups. |
| Infectious | The infectious cynicism spread throughout the team. |
| Poisonous | The poisonous atmosphere of the workplace led to high turnover. |
| Gangrenous | The gangrenous corruption had spread throughout the entire system. |
| Putrid | The putrid smell of decay permeated the abandoned building. |
| Nefarious | The nefarious activities of the organization were finally exposed. |
| Contagious | The contagious discontent spread rapidly among the workers. |
| Damaging | The damaging allegations ruined his career. |
| Eroding | The eroding influence of consumerism weakened traditional values. |
| Marring | The marring scandal tarnished the politician’s reputation. |
| Sullying | The sullying accusations damaged the company’s image. |
Usage Rules for Adjectives
When using adjectives for evil, it’s essential to adhere to standard grammatical rules. Adjectives typically precede the noun they modify, but can follow linking verbs.
Consider the following guidelines:
- Placement: Adjectives usually come before the noun (e.g., “a cruel tyrant”).
- Linking Verbs: After linking verbs (is, are, was, were, seems, etc.), adjectives describe the subject (e.g., “The tyrant was cruel”).
- Multiple Adjectives: When using multiple adjectives, follow the general order: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, purpose (e.g., “a vile, old, wooden chest”).
- Intensifiers: Adverbs can intensify adjectives (e.g., “extremely wicked”).
Exceptions to these rules are rare, but it is important to remember that context is everything. Sometimes, for stylistic effect, a writer might deviate from the standard order, but this should be done intentionally and sparingly.
Common Mistakes with Adjectives
One common mistake is using adjectives incorrectly after linking verbs. For example:
Incorrect: The plan was wickedly.
Correct: The plan was wicked.
Another mistake is misusing adverbs instead of adjectives:
Incorrect: He acted evil.
Correct: He acted evilly (adverb), or He was evil (adjective).
Also, be careful with adjective order when using multiple adjectives:
Incorrect: A wooden old vile chest.
Correct: A vile, old, wooden chest.
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding with the following exercises.
Exercise 1: Identifying Adjectives
Identify the adjectives for evil in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The corrupt politician was finally brought to justice. | Corrupt |
| 2. A sinister plot was uncovered by the detectives. | Sinister |
| 3. The devastating fire destroyed the entire forest. | Devastating |
| 4. His malicious intent was clear from his actions. | Malicious |
| 5. The demonic presence filled the room with dread. | Demonic |
| 6. The insidious rumors spread like wildfire. | Insidious |
| 7. The vile creature lurked in the shadows. | Vile |
| 8. The ruinous policies bankrupted the country. | Ruinous |
| 9. The baneful curse afflicted the entire family. | Baneful |
| 10. The perfidious ally betrayed his comrades. | Perfidious |
Exercise 2: Sentence Completion
Complete the following sentences with an appropriate adjective for evil.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The _______ dictator ruled with an iron fist. | Brutal |
| 2. The _______ crime shocked the entire nation. | Heinous |
| 3. The _______ witch cast a dark spell. | Maleficent |
| 4. The _______ scheme was designed to bankrupt the company. | Nefarious |
| 5. The _______ virus spread rapidly across the globe. | Deadly |
| 6. His _______ glare sent shivers down her spine. | Baleful |
| 7. The _______ rumors poisoned the atmosphere. | Noxious |
| 8. The _______ possession terrified the villagers. | Demonic |
| 9. The _______ propaganda slowly eroded public trust. | Insidious |
| 10. The _______ practices of the cult were exposed. | Degenerate |
Exercise 3: Adjective Modification
Modify the following sentences by adding an adjective for evil.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The plan was discovered. | The sinister plan was discovered. |
| 2. The queen plotted revenge. | The wicked queen plotted revenge. |
| 3. The fire destroyed the city. | The devastating fire destroyed the city. |
| 4. His words hurt her. | His malicious words hurt her. |
| 5. The presence filled the room. | The demonic presence filled the room. |
| 6. The influence spread quickly. | The insidious influence spread quickly. |
| 7. The creature emerged from the shadows. | The vile creature emerged from the shadows. |
| 8. The policies ruined the economy. | The ruinous policies ruined the economy. |
| 9. The curse afflicted the family. | The baneful curse afflicted the family. |
| 10. The ally betrayed his friends. | The perfidious ally betrayed his friends. |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, understanding the nuances of intensifiers, adjective order, and figurative language can further enhance their command of adjectives for evil.
Intensifiers with Adjectives
Intensifiers are adverbs that strengthen or weaken the meaning of adjectives. Common intensifiers include “very,” “extremely,” “incredibly,” “somewhat,” and “slightly.” For example:
- Very wicked
- Extremely sinister
- Incredibly malicious
- Somewhat evil
- Slightly baneful
Adjective Order
When using multiple adjectives, follow the general order: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, purpose. For example:
A vile, old, wooden chest (opinion, age, material)
Figurative Language
Adjectives for evil can be used figuratively to create vivid imagery and convey deeper meanings. For example:
“His heart was a black abyss,” where “black” is used metaphorically to describe a void of goodness.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between “evil” and “wicked”?While both words describe moral wrongness, “evil” often implies a deeper, more profound level of malevolence, while “wicked” can refer to mischievous or playfully bad behavior. However, both can be used to describe serious wrongdoing depending on the context.
- How do I choose the right adjective for evil?Consider the specific nuance you want to convey. Do you want to emphasize moral depravity, destructive force, malevolent intent, supernatural evil, or corrupting influence? Choose the adjective that best fits the context and intended impact.
- Can adjectives for evil be used in a positive context?Rarely. While figurative language can sometimes use negative adjectives in unexpected ways, adjectives for evil are generally reserved for describing negative concepts. Sarcasm or irony might employ them, but the underlying meaning remains negative.
- What is the difference between an adjective and an adverb for evil?Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns (e.g., “an evil plan”), while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs (e.g., “He acted evilly”). Make sure to use the correct form to avoid grammatical errors.
- How can I improve my vocabulary of adjectives for evil?Read widely, pay attention to the words authors use to describe negative characters and situations, and use a thesaurus to explore synonyms and related terms. Practice using new adjectives in your own writing to solidify your understanding.
- Are there any adjectives for evil that are considered outdated or archaic?Yes, some adjectives like “baleful” or “nether” may sound archaic to modern ears. While they can add a sense of historical or literary flair, be mindful of your audience and the overall tone of your writing. Ensure the archaic word fits the context appropriately.
- How do cultural differences affect the perception of adjectives for evil?Different cultures may have varying perceptions of what constitutes evil.
Therefore, some adjectives might carry different connotations or weight depending on the cultural context. Always be sensitive to these nuances and consider your audience when choosing adjectives for evil.
Conclusion
Mastering adjectives for evil enhances your ability to express complex ideas related to morality and wrongdoing. By understanding their definitions, structural roles, and appropriate usage, you can communicate with greater precision and impact.
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, complete with examples and exercises, to help you refine your vocabulary and writing skills. Continue to practice and explore these adjectives to deepen your understanding and effectively convey the nuances of evil in your communication.
